What do 'Secondary Readings' mean on the Orenda App?
The Orenda Calculator™ has an toggle to show or hide two additional chemistry values: pH ceiling and Carbonate Alkalinity.
The secondary readings toggle at the top-left allows users to "show" or "hide" secondary readings. Those secondary readings will appear beneath pH (pH ceiling) and Alkalinity (Carbonate Alkalinity).

To learn what these secondary readings are, you may notice they are underlined in the app. You can tap them because they are linked to a pop-up to learn more. But since you're here in our help center now, we'll explain them here too.
pH Ceiling
Beneath pH, the secondary reading called pH ceiling will appear. The pH ceiling is the upper pH limit in those current chemistry conditions. It is the pH of the water when carbon dioxide in the water has equalized with the carbon dioxide in the air, satisfying equilibrium per Henry's Law of the solubility of gasses.
In summary, because we have carbonate alkalinity in our water, our water is carbonated. Just like a carbonated soda or beer, our carbonated pools must go flat eventually. Flat simply means the CO2 in the water has equalized with the CO2 in the air, and therefore no more CO2 will leave the water.
Because of carbonate alkalinity, the amount of dissolved CO2 is a proxy for determining the concentration of Hydrogen ions (H+) in the water, which determines the pH. Simplified, the amount of dissolved CO2 determines the pH of the water.
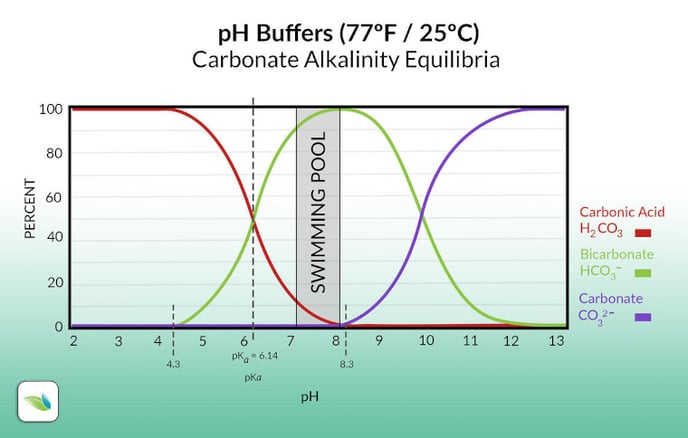
The pH ceiling is the pH of your water when it goes flat, meaning it cannot off-gas any more CO2 into the air. And speaking of carbonation, the second secondary reading is carbonate alkalinity itself.
Carbonate Alkalinity
Carbonate alkalinity is the sum of bicarbonate (HCO3-) and carbonate ions (CO32-). They are part of the carbonic acid/bicarbonate buffering system, which has a pKa value of 6.14.
Unlike Total Alkalinity (TA), which includes all dissolved alkali that can neutralize acids in water, carbonate alkalinity is limited to just bicarbonate and carbonate ions. Bicarbonate is in equilibrium with carbonic acid (H2CO3), which is dissolved CO2(aq).
The Orenda Calculator™ subtracts cyanurate alkalinity from TA (along with borates, if used) automatically. The carbonate alkalinity is also known as the "corrected" alkalinity because of these subtractions against TA.
The carbonate alkalinity and water temperature determine the pH ceiling.