What is the "pH Ceiling"?
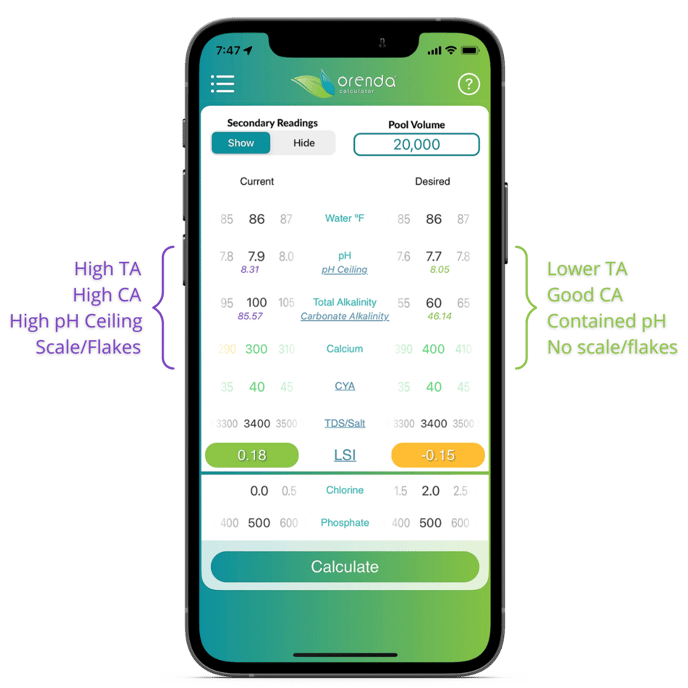
The Orenda Calculator® displays the pH ceiling as a real-time secondary read-out.
The pH Ceiling is the maximum pH your water can have when carbon dioxide has equalized with the air above the pool. It is technically called "pH(eq)", which stands for the pH at the equilibrium point when CO2 can no longer off-gas, and therefore the pH stops rising.
pH ceiling, CO2, and Henry's Law
Read this for more details on the physics of the pH ceiling.

Essentially, the amount of dissolved carbon dioxide in water determines the pH of the water:
The more CO2 dissolved in water, the lower the pH (and vice versa):
↑CO2 = ↓pH
↓CO2 = ↑pH
We go into more detail about pH here.
Henry's law basically states that any gas dissolved in a liquid must equalize with that same gas in the air above the liquid, based on pressure. We witness Henry's Law every time we open a carbonated drink. The CO2 bubbles leave the drink to equalize with the lower-pressured room (or outdoors), and eventually, the drink goes flat.
The same exact physics applies to swimming pools, though we don't see the bubbles. Our pools are far less carbonated than beer or soda.
Either way, when the CO2 in the water equalizes with the air above the water, the pH(eq) point is reached, and no more CO2 can leave the water. If it's forced out via aeration, the pressure of CO2 in the room will push CO2 right back into solution at the exact same rate it is lost. Physics can be pretty cool, huh?
Because CO2 determines the pH of water, the pH(eq) point is also the highest the pH can go. Because the less CO2, the higher the pH. That's why we at Orenda have coined pH(eq) as the pH Ceiling.
Why the Orenda Calculator® displays pH Ceiling
We believe it is to your advantage to know exactly how high the pH can eventually rise in your pool. You can plan accordingly and contain pH more reliably. We have a chart showing pH ceiling values, but few people have time to continue to reference the chart, then go back to the Orenda Calculator® screen, then make informed decisions. It was too many steps.
So we automated it and display the pH Ceiling in real-time as a secondary reading on the calculator. As you adjust the dials for pH, temperature, alkalinity, etc., the carbonate alkalinity will change too (another secondary reading). That carbonate alkalinity determines your pH ceiling at a given temperature. Here's the chart:
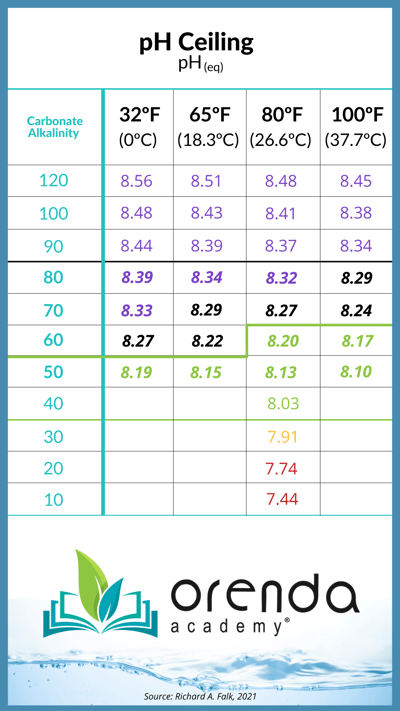
We decided to be more specific and extrapolate exact values for every single degree, and for carbonate alkalinities that fall between 10 ppm. In fact, the Orenda Calculator® factors in carbonate alkalinity as precise as two decimal places (i.e. 63.49 ppm). This precise carbonate alkalinity is then calculated along with water temperature to give an exact pH ceiling, which we then round to two decimal places for simplicity.
pH ceiling depends on Carbonate Alkalinity
The pH ceiling is dictated by the carbonate alkalinity, with one exception on the Orenda Calculator®. When you have either CYA or Borate in your water (or both), the carbonate alkalinity differs from total alkalinity. On the Orenda Calculator®, you will see that in this circumstance, changing the pH changes the carbonate alkalinity...but NOT the pH ceiling.
The reason for this is because of carbon dioxide. Indeed, pH will change the CYA and borate correction factors, but it does not actually change the pH ceiling. So it looks deceptive on the calculator when the carbonate alkalinity moves but pH ceiling does not. Don't worry, this is by design and is still accurate.
For more detailed tutorial on the Orenda Calculator®, check out our other articles in the learning center in the Orenda App section.